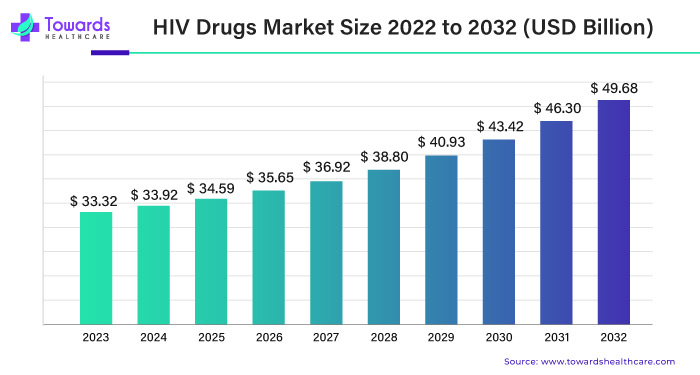
The pharmaceutical industry is witnessing a remarkable evolution, driven by advancements in medical science and a growing demand for effective treatments. One segment that has garnered significant attention is the market for HIV drugs. According to recent estimates, the HIV drugs market is poised for substantial growth, with projections indicating a surge from USD 33.32 billion in 2023 to over USD 49.68 billion by 2032, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% between 2024 and 2032. This essay aims to delve into the factors contributing to this anticipated growth, the challenges faced by the industry, and the implications for healthcare stakeholders.
Understanding the Dynamics of the HIV Drugs Market
1. Evolution of Treatment Strategies
The landscape of HIV treatment has evolved significantly since the discovery of the virus. Initially, the focus was primarily on managing symptoms and prolonging life expectancy. However, with advancements in medical research, the emphasis shifted towards developing antiretroviral therapies (ART) that could effectively suppress the replication of the virus, thereby reducing viral load and preventing disease progression. This shift in treatment paradigms has been instrumental in improving the quality of life for HIV patients and reducing mortality rates.
2. Expansion of Access to Treatment
Another significant factor driving the growth of the HIV drugs market is the concerted effort to expand access to treatment, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where the burden of HIV/AIDS is disproportionately high. Initiatives such as the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria have played a pivotal role in providing funding and technical support to scale up HIV treatment programs in resource-limited settings. As a result, more individuals living with HIV have been able to access life-saving medications, contributing to the overall market growth.
3. Technological Innovations and Pipeline Developments
The landscape of HIV drug development is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at introducing novel therapies with improved efficacy, safety, and tolerability profiles. Technological innovations, such as the development of long-acting injectable formulations and the exploration of new drug classes, hold promise for addressing the challenges of adherence and treatment resistance associated with current regimens. Additionally, the robust pipeline of investigational drugs targeting different stages of the HIV lifecycle underscores the industry’s commitment to addressing unmet medical needs and driving market growth.
For any queries, feel free to reach us @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/personalized-scope/5131
In today’s world, where medical knowledge and advancements have reached unprecedented heights, understanding diseases such as HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is crucial for maintaining public health and well-being. HIV weakens the body’s immune system, leaving individuals susceptible to various infections and diseases. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of HIV, from its transmission to its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, providing valuable insights for both medical professionals and the general public.
Transmission of HIV
HIV can be transmitted through various means, with the most common routes being:
1. Sharing Needles or Syringes
The sharing of needles or syringes among intravenous drug users remains one of the primary modes of HIV transmission. Contaminated needles can introduce the virus into the bloodstream, facilitating its spread from one individual to another.
2. Unprotected Sexual Contact
Engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse with an HIV-infected individual poses a significant risk of transmission. The virus can be present in bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and rectal fluids, making unprotected sex a potential avenue for HIV transmission.
3. Mother-to-Child Transmission
Pregnant women living with HIV can transmit the virus to their infants during childbirth or breastfeeding. Without proper medical intervention and preventive measures, mother-to-child transmission can occur, highlighting the importance of prenatal care and HIV screening for expectant mothers.
Symptoms of HIV
The symptoms of HIV can vary widely from person to person, and in some cases, individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms for years after infection. However, common early symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
As the virus progresses and the immune system weakens, more severe symptoms may manifest, including:
- Recurrent infections
- Rapid weight loss
- Night sweats
- Chronic diarrhea
It is important to note that the presence of these symptoms does not necessarily indicate HIV infection, as they can mimic other illnesses. Therefore, proper medical evaluation and testing are essential for accurate diagnosis.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis of HIV is paramount in managing the infection effectively and preventing its progression to AIDS. Timely medical intervention allows individuals to initiate antiretroviral therapy (ART) promptly. ART works by suppressing the virus, reducing its replication rate, and thereby preserving immune function.
Benefits of Early Treatment
- Viral Suppression: ART helps suppress the viral load, preventing further damage to the immune system.
- Disease Progression: Early treatment significantly reduces the risk of HIV progressing to AIDS.
- Transmission Prevention: Effective treatment lowers the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
Living with HIV
Contrary to popular misconception, being diagnosed with HIV is not a death sentence. With advancements in medical care and treatment, people living with HIV can lead fulfilling and productive lives. Comprehensive HIV management involves:
- Regular Medical Monitoring: Routine medical check-ups and monitoring of viral load and CD4 cell count are essential for assessing treatment effectiveness and overall health.
- Adherence to Treatment: Strict adherence to ART medication regimens is crucial for maintaining viral suppression and preventing drug resistance.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and avoiding harmful substances, can help bolster immune function and overall well-being.
Challenges and Opportunities
1. Access Barriers and Affordability
Despite significant progress in expanding access to HIV treatment, access barriers persist, particularly in low-resource settings. Limited healthcare infrastructure, supply chain challenges, and high medication costs remain significant hurdles to achieving universal access to HIV care and treatment. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving collaboration between governments, pharmaceutical companies, and non-governmental organizations to negotiate affordable pricing, strengthen healthcare systems, and improve supply chain management.
2. Treatment Adherence and Drug Resistance
Achieving optimal outcomes in HIV treatment hinges on strict adherence to medication regimens. However, maintaining adherence can be challenging due to factors such as pill burden, medication side effects, and socioeconomic barriers. Non-adherence not only compromises individual health outcomes but also contributes to the emergence of drug-resistant strains of HIV, posing a significant public health threat. Strategies to address adherence challenges include simplifying treatment regimens, providing adherence support services, and leveraging digital health technologies to monitor and support patient adherence.
3. Stigma and Discrimination
Stigma and discrimination continue to pose significant barriers to HIV prevention, testing, and treatment efforts worldwide. Fear of judgment and social exclusion deter individuals from seeking HIV testing and care, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment initiation. Addressing stigma and discrimination requires comprehensive strategies that focus on education, advocacy, and community engagement to promote acceptance, tolerance, and equitable access to healthcare services for all individuals, regardless of their HIV status.
Implications for Healthcare Stakeholders
1. Pharmaceutical Companies
For pharmaceutical companies operating in the HIV drugs market, the projected growth presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, expanding market demand and the introduction of new therapies offer the potential for revenue growth and market expansion. On the other hand, increasing competition, pricing pressures, and regulatory hurdles necessitate strategic agility and innovation to maintain a competitive edge. Furthermore, companies need to prioritize ethical considerations and corporate social responsibility initiatives to ensure equitable access to HIV
2. Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in delivering comprehensive HIV care and treatment services to patients. As the HIV drugs market continues to evolve, healthcare providers must stay abreast of the latest advancements in HIV treatment modalities, guidelines, and therapeutic options. This necessitates ongoing training and education to enhance clinical competencies and ensure the delivery of evidence-based, patient-centered care. Additionally, healthcare providers should actively engage in efforts to promote HIV testing, linkage to care, and retention in treatment to optimize health outcomes and prevent onward transmission of the virus.
3. Policymakers and Advocacy Groups
Policymakers and advocacy groups play a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of HIV care and treatment through the formulation of policies, allocation of resources, and advocacy for the rights and needs of people living with HIV. It is imperative for policymakers to prioritize investments in HIV prevention, treatment, and care programs, ensuring equitable access to essential services for all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status or geographic location. Furthermore, advocacy efforts aimed at combating stigma, discrimination, and human rights violations are essential for fostering an enabling environment conducive to effective HIV prevention and treatment efforts.
HIV Drugs Market Segment
By Drug Type
- Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
- Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
- Protease Inhibitors (PIs)
- Integrase Inhibitors
- Entry and Fusion Inhibitors
- Combination Class Drugs
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East and Africa
- South America
Unlock Infinite Advantages: Subscribe to Annual Membership
To own our PREMIUM study instantly, Click here @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5131
To Read More About HIV Drugs Market: