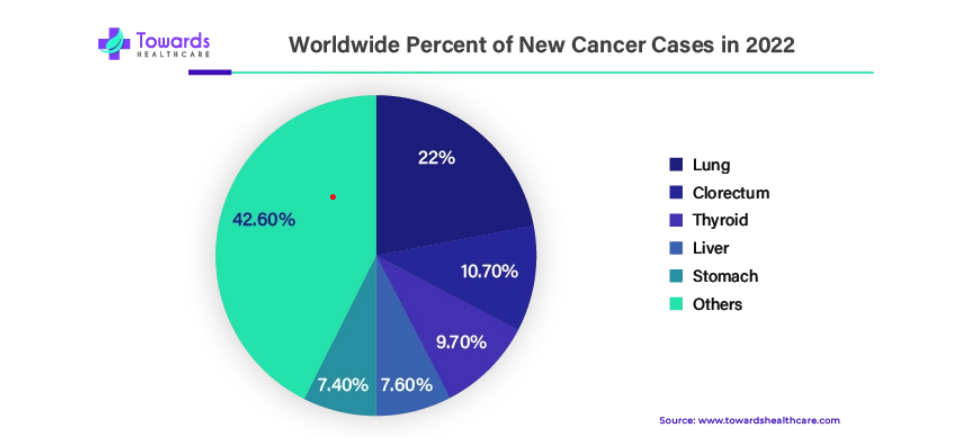
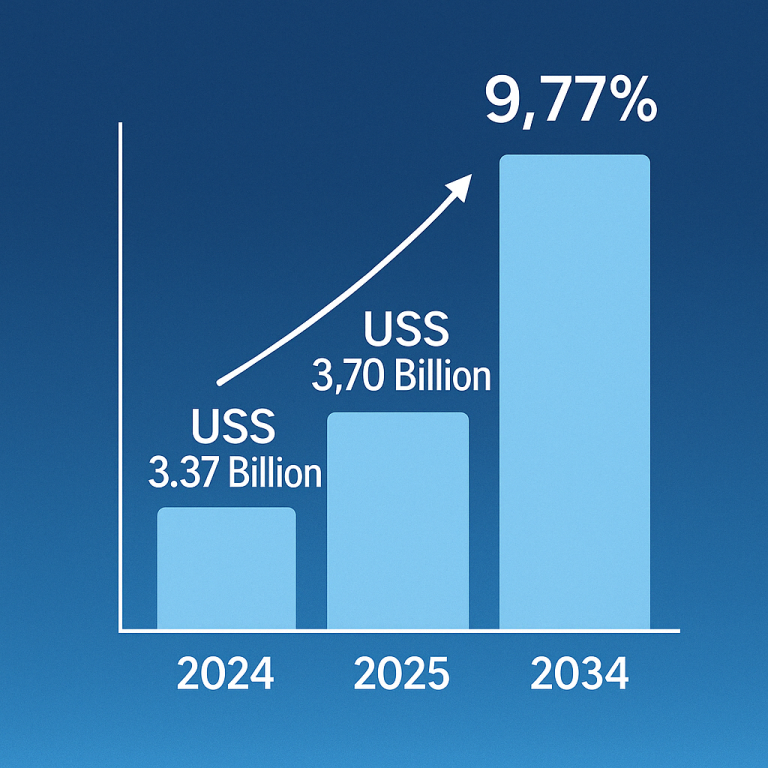
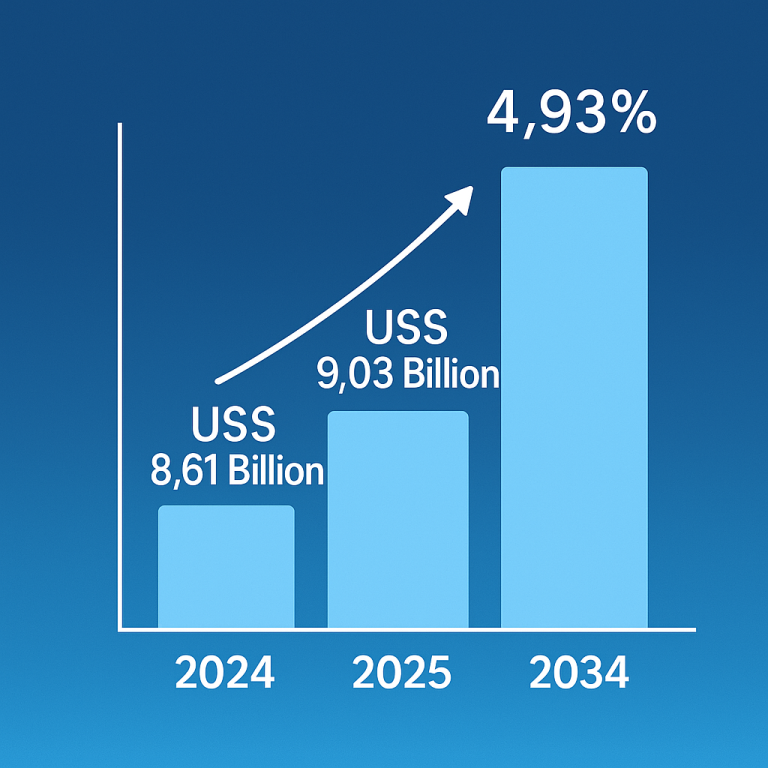
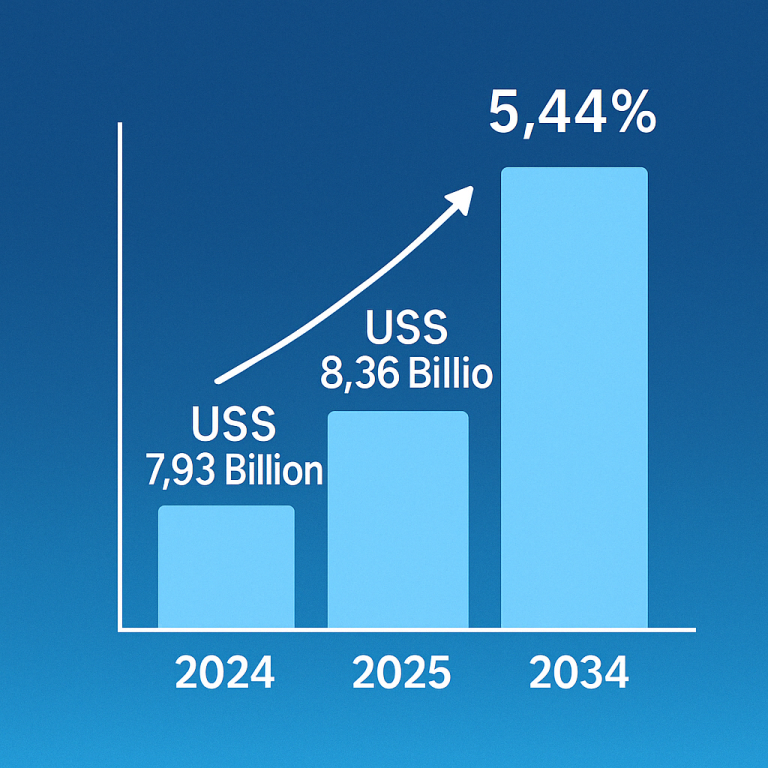
People with type 2 diabetes often struggle with excess fat production due to their liver’s inability to effectively regulate blood sugar levels. This condition, known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), can lead to liver inflammation, scarring, and eventually cirrhosis. Notably, individuals with type 2 diabetes face a significantly higher risk of developing liver cancer compared to those without diabetes.
A recent study from Stanford Medicine, conducted in February 2024, proposes a new approach to identifying type 2 diabetics at elevated risk of liver cancer who may not meet current screening criteria. Traditionally, liver cancer screening has focused primarily on individuals with cirrhosis, leaving out many high-risk individuals, particularly those with type 2 diabetes who may not yet have developed cirrhosis.
The implications of this study suggest a need for reevaluation of liver cancer screening protocols to include patients with diabetes. By expanding screening criteria, earlier detection of liver cancer could be achieved, leading to improved outcomes. Furthermore, this research may influence screening strategies for other diabetes-related cancers, such as breast cancer, highlighting the broader significance of early detection efforts in diabetes management.
Recent Therapy Advances
In recent years, significant advancements have emerged in cancer therapeutics, particularly concerning liver cancers. Major players in the field are actively researching and developing innovative treatment approaches through clinical trials and the creation of advanced therapies.
For example:
- In March 2024, Terumo, a Japan-based company, introduced B-TACE (Balloon-TACE), an advanced therapy designed for liver cancer management. Terumo’s B-TACE device, Occlusafe, facilitates the precise delivery of chemotherapy drugs to the tumor, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- In February 2024, Biosyngen’s BST02 received Fast Track Designation (FTD) from the US FDA, covering the treatment of various liver cancer forms, including cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- In January 2024, AstraZeneca’s EMERALD-1 Phase III trial reported positive outcomes. It showed that combining Imfinzi (durvalumab) with TACE and bevacizumab significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) among hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients eligible for embolization, compared to TACE alone.
- In November 2023, Terumo also launched B-TACE for liver cancer management, emphasizing its precision and reduced harm to healthy tissues.
Targeted Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) stands out as the most prevalent form of primary liver cancer, accounting for 90% of all reported cases. Despite constituting only 3% of 5-year survival rates, it ranks third in cancer-related mortality. While systemic therapy has shown some clinical improvements in advanced stages, the prognosis remains grim. The emergence of novel molecular-targeted medications in recent decades has shown promising results in clinical trials. However, there’s a pressing need for further research into new treatments given the limited benefits and poor prognoses associated with current systemic therapy. This underscores the importance of targeted and advanced therapies.
The landscape of HCC treatment has undergone significant transformation over the past 16 years, primarily due to major advancements in targeted therapy. Key factors driving this evolution include:
- Introduction of Sorafenib (2007): Sorafenib, the first effective and approved targeted therapy for advanced HCC, marked a pivotal moment in liver cancer treatment. Its success paved the way for further therapeutic developments.
- Emerging Treatment Options: New targeted drugs like Lenvatinib and the combination of Bevacizumab and Atezolizumab have emerged as viable first-line treatment options for advanced HCC patients, building on the efficacy of Sorafenib. Additionally, the introduction of Ramucirumab, Regorafenib, and Cabozantinib (specifically for patients with AFP > 400 ng/mL) has significantly broadened the therapeutic arsenal available for patients undergoing second-line treatment.
These advancements have provided patients with advanced HCC with improved treatment outcomes and a more optimistic prognosis.
To own our research study instantly, Click here @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5146
Read more about Liver Cancer Drugs Market:
Unlock Infinite Advantages: Subscribe to Annual Membership
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact us at sales@towardshealthcare.com
About Us
Healthcare Web Wire is a premier subsidiary of Towards Healthcare, dedicated to providing comprehensive insights and information related to the healthcare industry. With a commitment to delivering accurate and timely updates, Healthcare Web Wire serves as a vital resource for professionals, enthusiasts, and stakeholders within the healthcare sector. Our platform serves as a central hub for the latest news, trends and developments shaping the healthcare landscape. Join us on Healthcare Web Wire and become part of a vibrant community dedicated to advancing healthcare knowledge and shaping the future of healthcare worldwide.
Explore the comprehensive statistics and insights on healthcare industry data and its associated segmentation: Get a Subscription
For Latest Update Follow Us: https://www.linkedin.com/company/towards-healthcare