Driving Factors and Innovations in Non-Small Lung Carcinoma Market Trends
Smoking as the Prime Catalyst for NSCLC Incidence and Its Impact on Market Growth
Smoking stands out as the predominant cause behind a multitude of cancers, notably lung, stomach, pancreas, esophagus, mouth, voice box, throat, leukemia, rectum, colon, cervix, and bladder, attributing to 85% of cancer cases. Notably, smoking emerges as the leading cause of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC), with a staggering 95% of cases deemed preventable through stringent smoking restrictions. To counteract this, various governments have implemented anti-smoking policies, including bans on tobacco advertisements.
According to the World Health Organization, tobacco product usage affects approximately 1.3 billion individuals, resulting in 8 million smoker deaths and 1.3 million deaths among second-hand smokers annually.
Challenges Impeding NSCLC Treatment Market Expansion Due to High Costs
The formidable expenses associated with carcinoma treatment stem from multiple factors. Primarily, the extensive investment in drug development, encompassing clinical trials and research & development, contributes significantly to treatment costs. Additionally, the specialized expertise of healthcare professionals involved in these procedures leads to substantial compensation demands. Furthermore, the advanced technology and infrastructure utilized in cancer treatment escalate expenses. This financial burden poses a significant challenge, particularly for individuals from low- and middle-income countries, where 80% of active smokers reside, as per WHO statistics.
Download a sample of this report @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/personalized-scope/5155
Minimally Invasive Surgery as a Growth Catalyst in the NSCLC Market
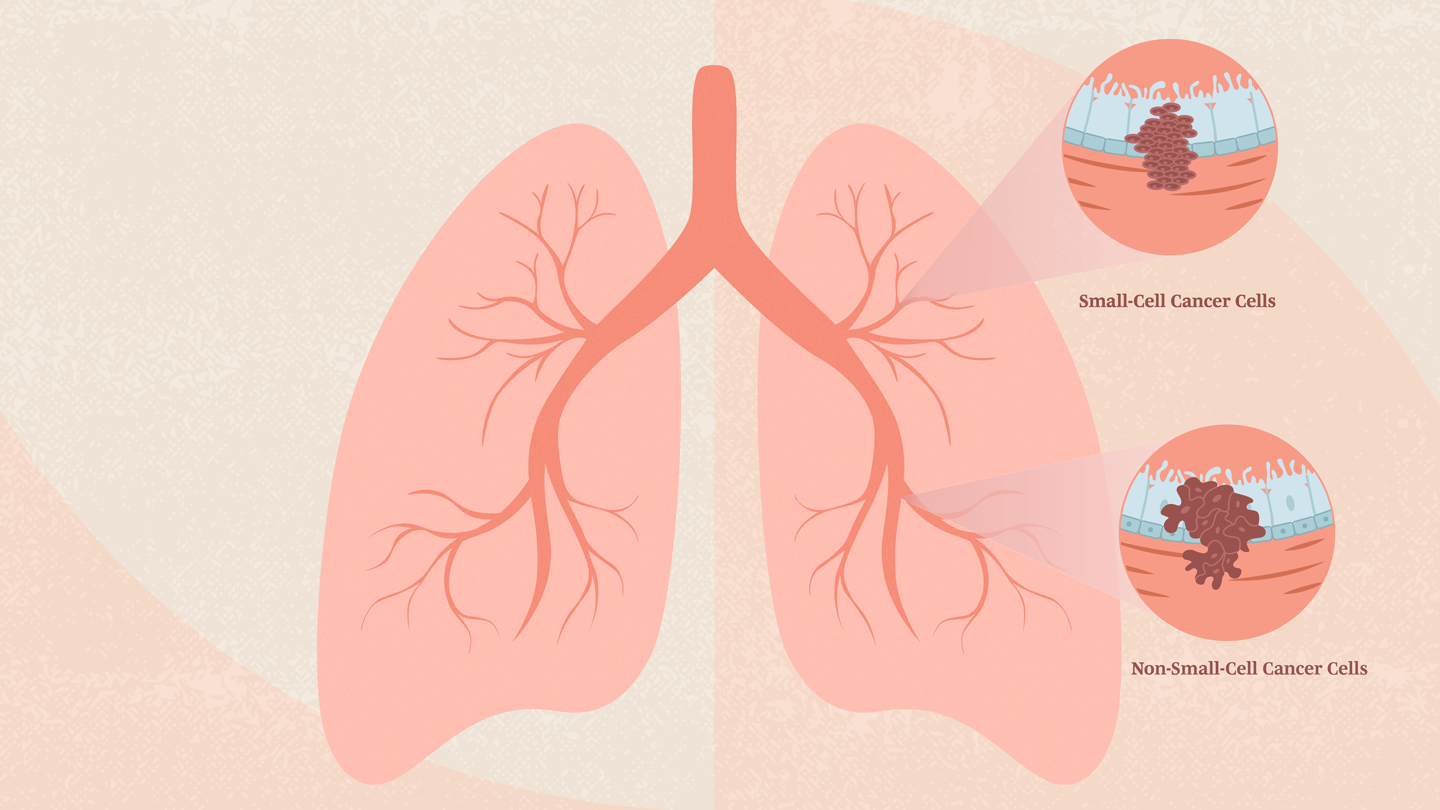
The advent of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionized the field of surgery over the past two decades. Specifically, techniques such as robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS) and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) have emerged as the standard for thoracic surgeries, particularly in early-stage lung cancer cases. Despite these advancements, concrete evidence comparing the therapeutic outcomes of minimally invasive techniques to traditional open surgery remains scarce. However, with the proliferation of lung cancer screening programs leading to increased early detection, the frequency of minimally invasive procedures is expected to surge, thereby driving growth in the non-small lung carcinoma market.
Illustrative Examples of Innovative Advancements:
- In March 2024, Porter expanded its repertoire of advanced medical treatments for lung ailments to include robotic-assisted lung biopsies. This cutting-edge technology offers patients a less invasive means of obtaining precise diagnostic information, marking a significant milestone in early lung cancer detection and treatment.
- In January 2024, with the collaboration of Shanghai medical professionals, surgeons in Zhejiang Province conducted the first minimally invasive lung cancer procedure under acupuncture anesthesia. Employing a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)-based approach, the surgery utilized a tubeless method to minimize patient stress and promote expedited recovery. Notably, the 67-year-old patient was able to walk back to her ward post-treatment, underscoring the potential of innovative techniques in enhancing patient outcomes.