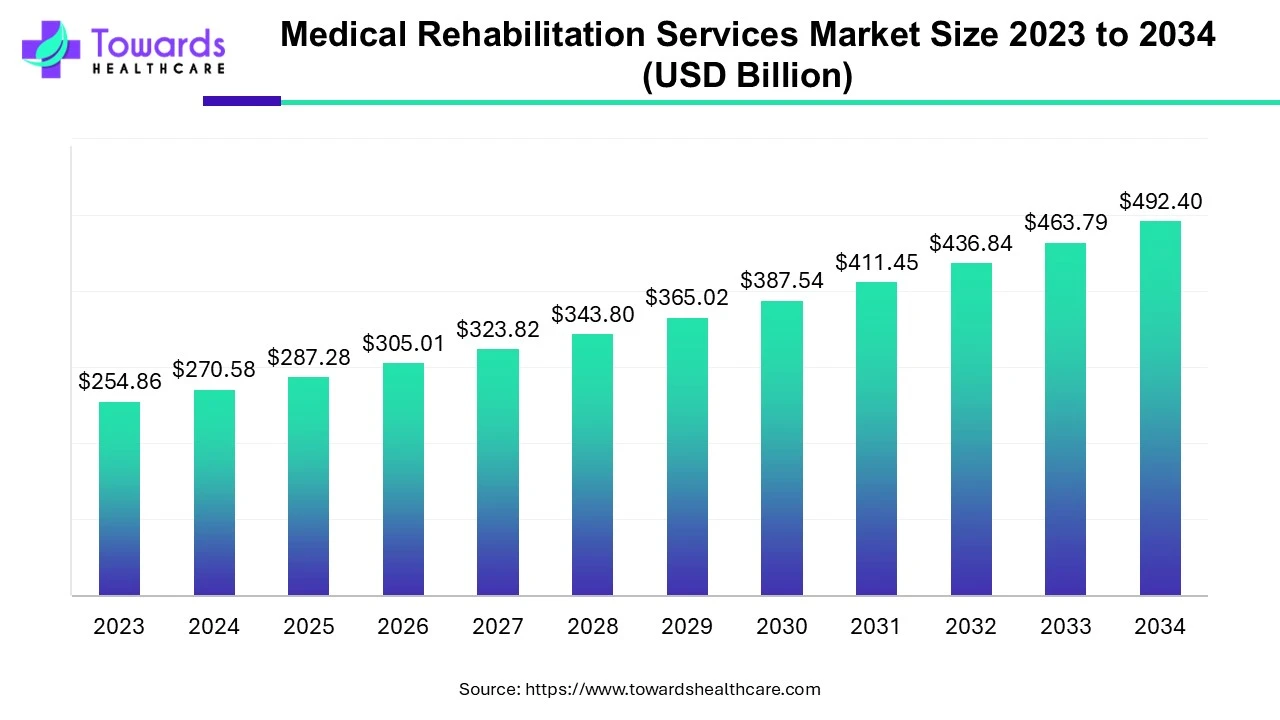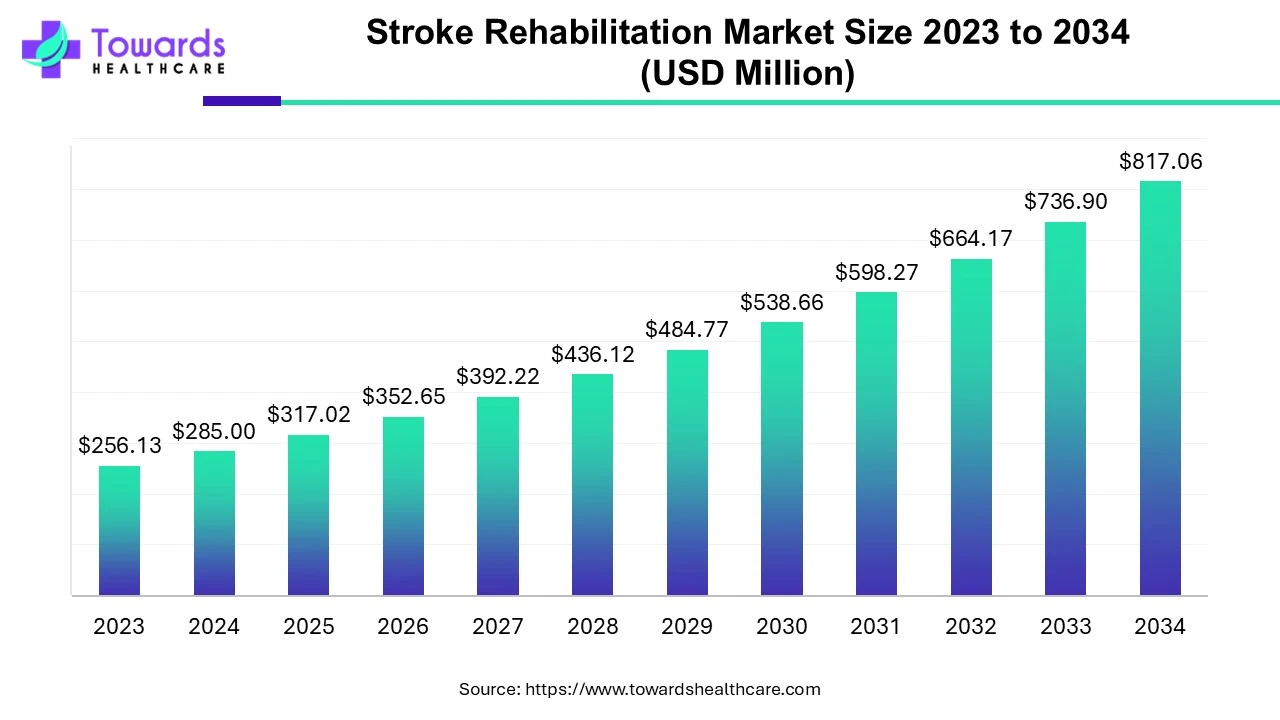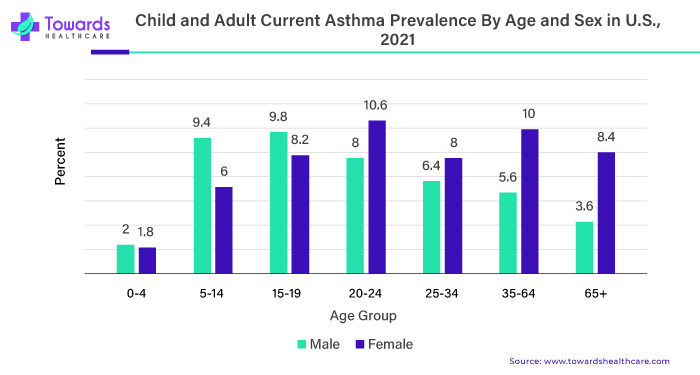
Corticosteroids, a cornerstone in the management of respiratory ailments, are frequently employed by pulmonologists. The method of administering these medications directly into the lungs offers significant advantages in treating conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), contributing to the growth of the corticosteroid market.
Addressing the Prevalence of Respiratory Diseases
In the year 2020 alone, approximately 1 million individuals sought emergency care for asthma, with around 94,560 requiring hospitalization due to the severity of their condition. This staggering prevalence underscores the urgent need for effective treatments. Corticosteroids stand as a common prescription for pulmonary disorders, given the widespread occurrence of these diseases.
For any queries feel free to reach us @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/personalized-scope/5111
Enhanced Treatment through Localized Delivery
A notable advantage of pulmonary application is its targeted delivery, directing corticosteroids precisely to the lungs where inflammation commonly manifests in respiratory conditions. This localized approach minimizes systemic exposure, thereby reducing the risk of systemic side effects while maximizing therapeutic impact at the site of inflammation. In comparison to systemic administration methods such as oral or injectable forms, inhaled corticosteroids demonstrate lower systemic absorption, mitigating systemic side effects such as bone loss or immune system suppression. Consequently, inhaled corticosteroids emerge as a preferred long-term treatment option for chronic respiratory conditions.
Managing Inflammation and Improving Symptom Control
Inhaled corticosteroids play a crucial role in managing airway inflammation, a fundamental aspect of respiratory diseases like asthma and COPD. The efficacy of these medications is evident in improved symptom control, reduced exacerbations, and enhanced lung function. Moreover, the patient-friendly nature of inhaled corticosteroids, typically administered through inhalers, promotes increased patient compliance with prescribed treatment regimens. This adherence is essential for effectively managing chronic respiratory conditions.
Future Perspectives and Research Endeavors
The success of inhaled corticosteroids in managing respiratory conditions has spurred ongoing research into their potential application in other pulmonary disorders. This exploration holds promise for expanding the range of indications for inhaled corticosteroids, further driving their demand in the market.
Corticosteroids administered via pulmonary routes represent a cornerstone in the management of respiratory ailments, offering targeted treatment, improved symptom control, and enhanced patient compliance. As research continues to unfold, the potential applications of these medications in diverse pulmonary disorders are poised to revolutionize respiratory care.
Combination therapies, wherein inhaled corticosteroids are paired with other respiratory medications like long-acting beta-agonists, offer a comprehensive approach to managing respiratory conditions. This integration contributes to the diversity of the market for respiratory medicines.
| Sr. No. | Combination Therapy | Indication |
| 1. | Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) with long-acting bronchodilators (LABA) | This combination is frequently used for asthma. The LABA opens airways while the ICS reduces inflammation. Examples include fluticasone/salmeterol (Advair) and budesonide/formoterol (Symbicort). |
| 2. | ICS with long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) | This combination is commonly used for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), another type of inflammatory lung disease. It targets different aspects of airway relaxation compared to ICS/LABA. Examples include fluticasone/umeclidinium/vilanterol (Trivento) and beclomethasone/glycopyrrolate/formoterol (Breztri Aerosphere). |
| 3. | Systemic Corticosteroids | These are typically used for short-term management of severe exacerbations of various pulmonary diseases, including asthma and COPD. They reduce inflammation but have more side effects than inhaled corticosteroids. |
| 4. | Triple Therapy | Combining ICS, LABA, and LAMA is sometimes used for patients with severe or poorly controlled COPD. This approach targets multiple mechanisms involved in the disease. |
As respiratory conditions remain prevalent worldwide, the demand for targeted and effective treatments like inhaled corticosteroids is expected to drive the growth of the corticosteroid market. Ongoing developments in formulations, devices, and combination therapies further enhance the market potential for the pulmonary application of corticosteroids.
Take a smart decision to own our advanced research study @ https://www.towardshealthcare.com/price/5111
Access our Premium Real Time Data Intelligence Tool, Visit: www.precedencestatistics.com
Related Snapshots of the Report: