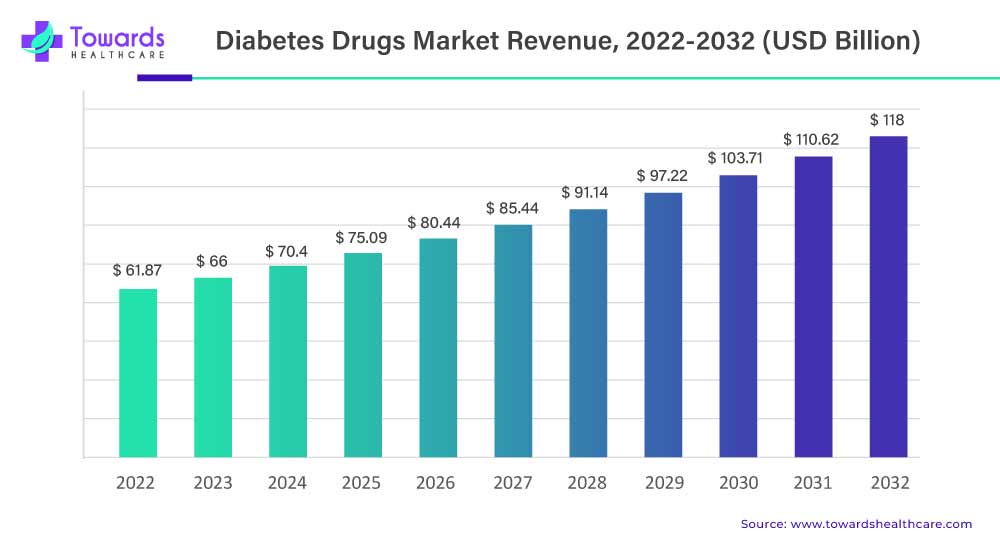
In the dynamic landscape of healthcare, the global diabetes drugs market is poised for an unprecedented surge. With an estimated value of USD 61.87 billion in 2022, this market is projected to experience a remarkable 6.7% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) from 2023 to 2032, culminating in an impressive USD 118 billion by 2032. This phenomenal growth is fueled by the escalating prevalence of diabetes and the unwavering support extended to patients worldwide.
More than 75% of diabetic adults reside in countries with low or middle incomes.
The diabetes drugs market refers to the pharmaceutical market dedicated to the development, production, and sale of drugs used for the treatment of diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, either due to inadequate production of insulin or the body’s inability to effectively use insulin. In 2021, there were approximately 537 million adults living with diabetes, representing 1 in 10 individuals.
Projections indicate that this number is expected to increase to 643 million by 2030 and further to 783 million by 2045, emphasizing the alarming growth and global impact of diabetes as a prevalent health condition.

Pervasive Expansion: A Closer Look at the Numbers
1. Escalating Market Valuation
The projected leap from USD 61.87 billion in 2022 to an estimated USD 118 billion by 2032 underscores the robust expansion underway. This substantial increase is indicative of the soaring demand for innovative diabetes drugs market in the globe.
2. Impressive CAGR of 6.7%
The compound annual growth rate of 6.7% forecasted for the period between 2023 and 2032 is a testament to the sustained upward trajectory of the diabetes drugs market. This steady growth rate signifies a flourishing industry, propelled by evolving healthcare needs and technological advancements.
The market for diabetes drugs is driven by several factors. Firstly, the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide is a significant driver of market growth. The growing incidence of obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and unhealthy dietary habits have contributed to the rise in diabetes cases. As a result, there is a higher demand for effective drugs to manage and control blood sugar levels.
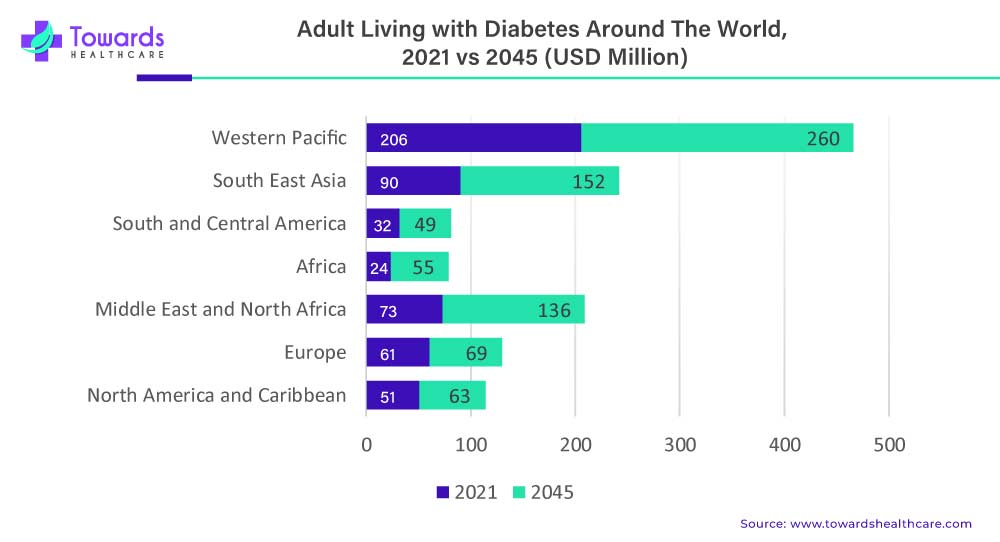
Driving Forces: Unraveling the Factors Behind the Surge
1. Mounting Prevalence of Diabetes
One of the primary drivers behind the surge in the diabetes drugs market is the escalating prevalence of diabetes worldwide. As the number of individuals grappling with this metabolic disorder continues to rise, the demand for effective pharmaceutical interventions intensifies, catalyzing market expansion.
2. Rising Patient Support: A Pillar of Growth
The unwavering support extended to diabetes patients plays a pivotal role in propelling the market forward. Increased awareness, advocacy, and patient-centric initiatives contribute to a conducive environment for the development and adoption of cutting-edge diabetes drugs market.
Moreover, the advancements in medical research and the understanding of diabetes have led to the development of innovative drug therapies. Pharmaceutical companies are investing in research and development activities to discover new and improved diabetes drugs market. These advancements include the development of novel drug classes, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and DPP-4 inhibitors, which provide better glycemic control and fewer side effects compared to traditional therapies.
The Role of Type 2 Diabetes in the Diabetes Drugs Market
Type 2 diabetes accounts for the majority of diabetes cases worldwide, making it the largest segment within the diabetes drugs market. The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes, particularly due to lifestyle factors and aging populations, has led to a significant patient population requiring pharmacological interventions to manage their condition. In 2021, a significant number of adults, specifically 541 million individuals, have reported having Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT). This condition indicates a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This sizable patient base contributes to the overall market size and demand for diabetes drugs.
A Glimpse into the Future: Anticipated Market Dynamics
1. Technological Innovations
The future landscape of the diabetes drugs market is anticipated to be shaped by continuous technological innovations. Advancements in drug delivery mechanisms, diagnostic tools, and treatment modalities are expected to redefine the standards of care for individuals managing diabetes.
2. Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Solutions for Maximum Impact
The shift towards personalized medicine is poised to revolutionize diabetes treatment. Tailoring interventions based on individual patient profiles and genetic makeup promises more targeted and efficient therapeutic outcomes, further amplifying the market’s growth potential.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that typically requires long-term management. Individuals with type 2 diabetes often rely on pharmacological interventions to control blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications. This ongoing treatment demand for type 2 diabetes drives the continuous use of diabetes drugs market and creates a consistent revenue stream for pharmaceutical companies operating in the market.
The prevalence and impact of type 2 diabetes have spurred extensive research and development efforts in the pharmaceutical industry. There is a continuous focus on developing novel and more effective medications for type 2 diabetes, including advancements in drug classes, formulations, and delivery methods. This ongoing research and innovation drive the growth of the diabetes drugs market, with pharmaceutical companies striving to provide improved treatment options for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes management involves a multifaceted approach that includes medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Healthcare providers emphasize the importance of disease management to prevent complications and improve overall health outcomes for individuals with type 2 diabetes. This focus on comprehensive care and the adoption of integrated treatment strategies contribute to the sustained demand for diabetes drugs market.
On the other hand, while type 2 diabetes is more prevalent, type 1 diabetes also plays a significant role in the diabetes drug market. In 2022, approximately 62% of all new cases of Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) were reported in individuals aged 20 years or older. This highlights that T1D can affect individuals beyond childhood and adolescence, contrary to the common perception that it primarily occurs in younger age groups. The increasing prevalence of T1D in adults emphasizes the need for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies tailored to this specific population to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Role of Patient Support and Education in the Diabetes Drugs Market
Patient support and education play a significant role in the growth of the generic drugs market. Patient support and education programs aim to improve medication adherence among patients taking generic drugs. Adherence to prescribed medication regimens is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes and cost savings. Patient support initiatives, such as counseling services, reminder systems, and educational materials, help patients understand the importance of medication adherence and provide them with tools and resources to stay on track with their treatment.
Patient education programs raise awareness about generic drugs and their benefits, including cost savings, accessibility, and comparable efficacy to brand-name drugs. By educating patients about the safety, quality, and effectiveness of generic drugs, healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies can increase patient acceptance and confidence in using these medications. This, in turn, drives market growth as more patients opt for generic drugs instead of higher-priced brand-name alternatives.
Patient support programs focus on making generic drugs more affordable and accessible to patients. This includes initiatives such as patient assistance programs, co-pay assistance, and drug discount cards. By addressing financial barriers, patient support initiatives help ensure that patients can access and afford their prescribed medications, promoting wider adoption of generic drugs in the market.
Thus, patient support, and education programs have a positive impact on the growth of the generic drugs market. By improving medication adherence, raising awareness and acceptance, enhancing affordability and accessibility, promoting disease management and self-care, and addressing health literacy, these initiatives empower patients to choose generic drugs and contribute to market expansion.
Impact of Patent Expiration in the Diabetes Drugs Market
Patent expiration is a significant factor that can impact the diabetes drugs market. When the patents for branded diabetes drugs expire, it allows other pharmaceutical companies to develop and market generic versions of the drugs. This results in increased competition within the market. The expiration of patents for branded diabetes drugs market leads to the entry of generic alternatives, which are typically offered at lower prices. Generic drugs are bioequivalent to their branded counterparts, meaning they have the same active ingredients and therapeutic effects. The availability of lower-cost generic options provides cost savings for patients, healthcare systems, and insurers, making diabetes treatment more affordable and accessible.
As generic drugs enter the market, the market share and revenue of the branded drugs may decline. This can pose challenges for pharmaceutical companies that previously held exclusive rights to their patented drugs. They may experience a loss of market exclusivity and face increased competition from generic manufacturers. However, patent expiration can also present opportunities for pharmaceutical companies.
Some companies strategically plan for patent expirations by developing new formulations or combinations of existing drugs, securing additional indications or therapeutic uses, or investing in research and development to bring innovative products to market. By leveraging their expertise and resources, companies can navigate the challenges posed by patent expiration and maintain their market position.
Thus, patent expiration in the diabetes drugs market stimulates competition and can lead to lower prices, increased access to medications, and improved affordability for patients. It encourages innovation and drives the development of new treatment options. While it may pose challenges for branded drug manufacturers, it also opens doors for new players and stimulates market dynamics that benefit patients and healthcare systems.
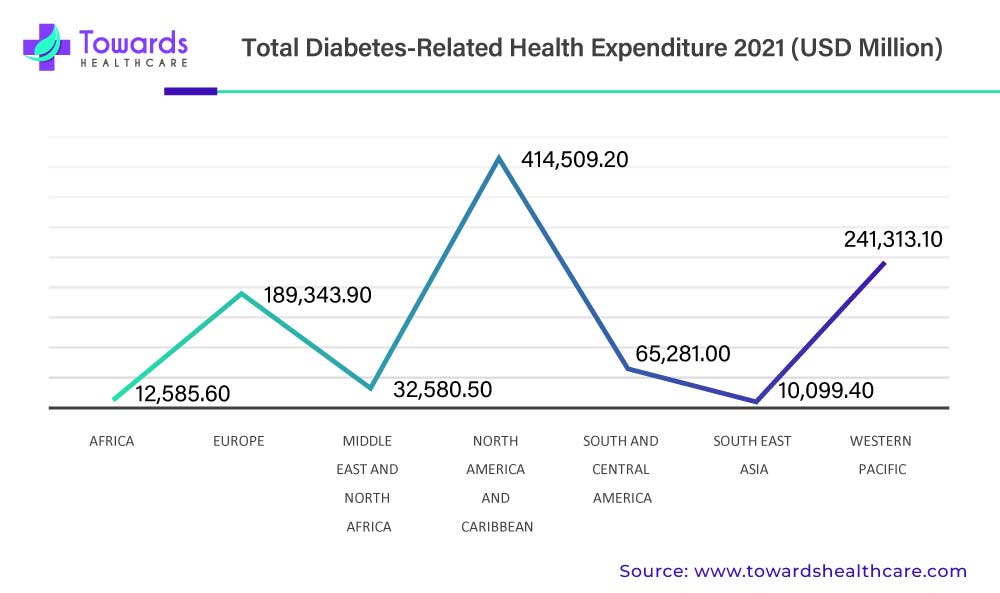
The North American region, particularly the United States, holds a significant share of the diabetes drugs market. Factors such as the high prevalence of diabetes, well-established healthcare infrastructure, favorable reimbursement policies, and a large diabetic patient population drive market growth in this region. The presence of major pharmaceutical companies and ongoing research and development activities further contribute to market expansion. The United States has a high prevalence of diabetes, with millions of people affected by the disease. This large diabetic population creates a substantial demand for diabetes drugs market and related healthcare services.
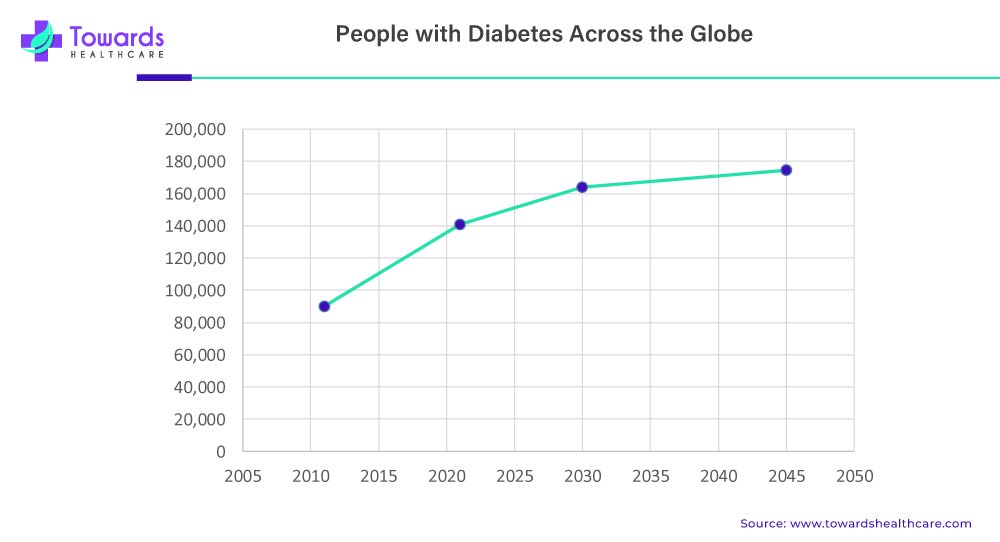
Role of Technological Advancements in the Diabetes Drugs Market
Technological advancements present significant opportunities in the diabetes drugs market. Continuous glucose monitoring devices have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time information about blood glucose levels. These devices eliminate the need for frequent fingerstick measurements and allow individuals to make immediate treatment adjustments. The integration of CGM data with insulin pumps and automated insulin delivery systems has the potential to enhance glycemic control and improve patient outcomes. Pharmaceutical companies can explore partnerships or develop their own CGM technologies to complement their diabetes drug offerings.
In addition, Digital therapeutics, including mobile applications and software programs, offer interactive and personalized interventions to support diabetes management. These solutions can provide educational resources, behavior change support, medication adherence reminders, and lifestyle tracking features. Pharmaceutical companies can leverage digital therapeutics to enhance patient engagement, improve treatment adherence, and collect valuable real-world data for drug development and optimization.
Furthermore, AI and machine learning technologies have the potential to revolutionize diabetes care. These technologies can analyze large volumes of patient data, identify patterns, and generate insights that assist in personalized treatment recommendations. AI-powered algorithms can help optimize insulin dosing, predict hypoglycemic events, and identify individuals at high risk of developing complications. Pharmaceutical companies can collaborate with technology firms or invest in AI capabilities to enhance the effectiveness and precision of their diabetes drug therapies.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, offer opportunities for continuous health monitoring and data collection. These devices can track physical activity, sleep patterns, heart rate, and other relevant parameters. By integrating wearable devices with diabetes management platforms, pharmaceutical companies can gather valuable data to understand patient behaviors, tailor treatment strategies, and provide personalized support.
Telemedicine has gained significant momentum, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Remote consultations and virtual monitoring allow healthcare professionals to connect with patients in real-time, monitor their diabetes management remotely, and provide timely interventions. Pharmaceutical companies can collaborate with telemedicine platforms or develop their own remote patient monitoring solutions to enhance patient access to care and support long-term diabetes management.
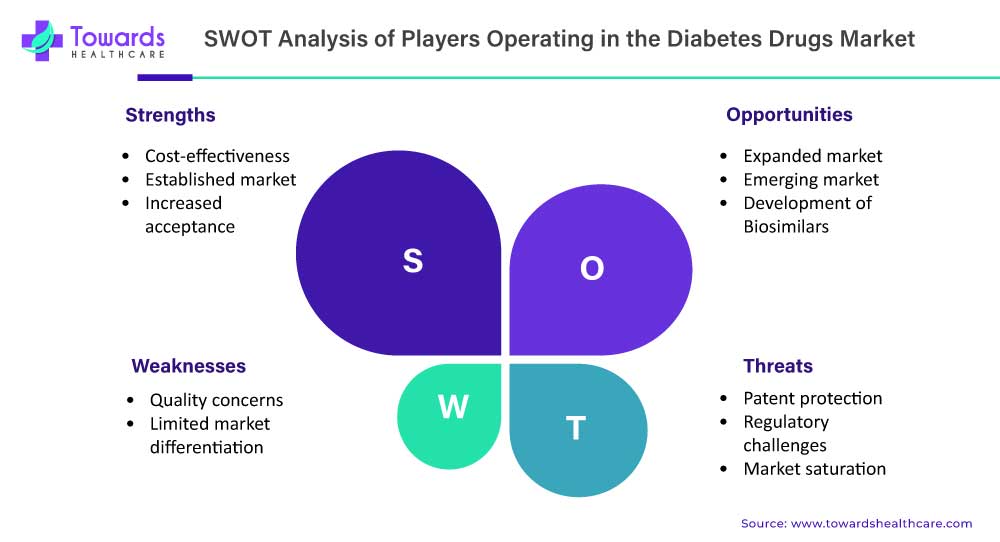
Regional Landscape of Diabetes Drugs Market
A significant majority, specifically over 3 in 4 adults with diabetes, reside in low- and middle-income countries. This highlights the disproportionate burden of diabetes on these regions, emphasizing the importance of addressing healthcare disparities and improving access to diabetes management and prevention resources in those areas.
Strengths:
- Generic drugs are generally more affordable compared to their branded counterparts, making them accessible to a larger population.
- The generic drugs market has a well-established presence and is recognized as an essential component of healthcare systems worldwide.
- There is a growing acceptance and trust in generic drugs among patients, healthcare professionals, and regulatory authorities.
Weaknesses:
- Some stakeholders may have concerns about the quality and efficacy of generic drugs, although they undergo rigorous regulatory scrutiny and quality control.
- Generic drugs often have similar formulations and therapeutic effects, making it challenging for manufacturers to differentiate their products.
Opportunities:
- The demand for generic drugs is expected to increase due to factors such as the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, the aging population, and cost-containment efforts in healthcare.
- There is a significant opportunity for growth in emerging markets, where access to affordable healthcare is a major concern.
- The development and commercialization of biosimilars, which are generic versions of biologic drugs, present new opportunities for market expansion.
Threats:
- The expiration of patents on branded drugs may lead to increased competition from generic manufacturers, posing a threat to market share and profitability.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements and the need for extensive clinical trials can be time-consuming and costly for generic drug manufacturers.
- The generic drugs market may become saturated in some therapeutic areas, limiting growth potential.
Competitive Landscape:
The diabetes drugs market is highly competitive, with several key players competing for market share. These companies focus on developing innovative drugs and treatments to meet the evolving needs of patients with diabetes. Several key players dominate the competitive landscape in this field. To gain a larger share of the market, players are using strategies like investments, alliances, acquisitions, and mergers.
Some major players involved in the diabetes drugs market are Novo Nordisk A/s, Sanofi, Merck & Co, Inc, Eli Lilly and Company, AstraZeneca, Takeda Pharmaceuticals Company Limited, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Novartis AG, Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc., and Bayer AG.
Market Segmentation:
By Drug Class
- Insulin
- DPP- 4 Inhibitors
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
- SGLT2 Inhibitors
By Diabetes Type
- Type 1
- Type 2
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Subcutaneous
- Intravenous
By Distribution Channel
- Online pharmacies
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail pharmacies
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Conclusion: Navigating the Upward Trajectory
In conclusion, the global diabetes drugs market is on a transformative journey, fueled by factors such as the escalating prevalence of diabetes and heightened patient support. The projected growth, characterized by a robust CAGR of 6.7%, highlights the resilience and dynamism of this market. As technological innovations and personalized medicine take center stage, the future promises a landscape where diabetes management is not just about treatment but about tailored solutions for individual well-being.